The way Malaysians search for information has fundamentally changed. When someone in Kuala Lumpur searches for “best accounting software for SME”, they no longer see just ten blue links. Instead, Google’s AI generates a comprehensive answer that pulls information from multiple sources, compares features, and even suggests alternatives based on business size and industry.
This shift represents more than a cosmetic update to search results. It signals a transformation in how search engines understand, evaluate, and present information. For Malaysian businesses competing in increasingly crowded digital markets, understanding AI SEO is no longer optional.
This guide breaks down AI SEO into practical, actionable strategies specifically designed for the Malaysian context, where businesses operate across multiple languages, serve diverse communities, and face unique local search challenges.
What Exactly Is AI SEO And How Is It Different From Traditional SEO
AI SEO represents a dual transformation in how we approach search engine optimisation. On one side, it involves using AI tools to improve your SEO workflow, making research faster, content production more efficient, and technical optimisation more precise. On the other side, and perhaps more critically, it means making your website “AI ready” so that AI-powered search engines can easily understand, trust, and reuse your content in their generated answers.
Traditional SEO focused primarily on matching keywords to queries and earning backlinks to boost page authority. You optimised for specific keyword phrases, built links pointing to specific URLs, and measured success through rankings for those exact terms. The game was relatively straightforward: identify what people search for, create pages targeting those searches, and convince Google that your page deserves to rank.
AI SEO operates on different principles. Modern AI systems don’t just match keywords; they understand context, intent, and relationships between concepts. They break your content into semantic blocks, convert these blocks into mathematical representations called vectors or embeddings, and then retrieve and synthesize information from multiple sources to answer complex queries.
Consider a practical Malaysian example. A traditional SEO approach for a car rental company in Langkawi might target the keyword “kereta sewa Langkawi murah” with a dedicated landing page. An AI SEO approach would ensure that same company’s content addresses the full spectrum of questions a visitor might have: what documents are needed, whether international licenses are accepted, what insurance options exist, how to handle toll payments, and what the fuel policy is. This comprehensive coverage allows AI systems to reference your content when answering related questions, even if the user’s query doesn’t exactly match your targeted keywords.
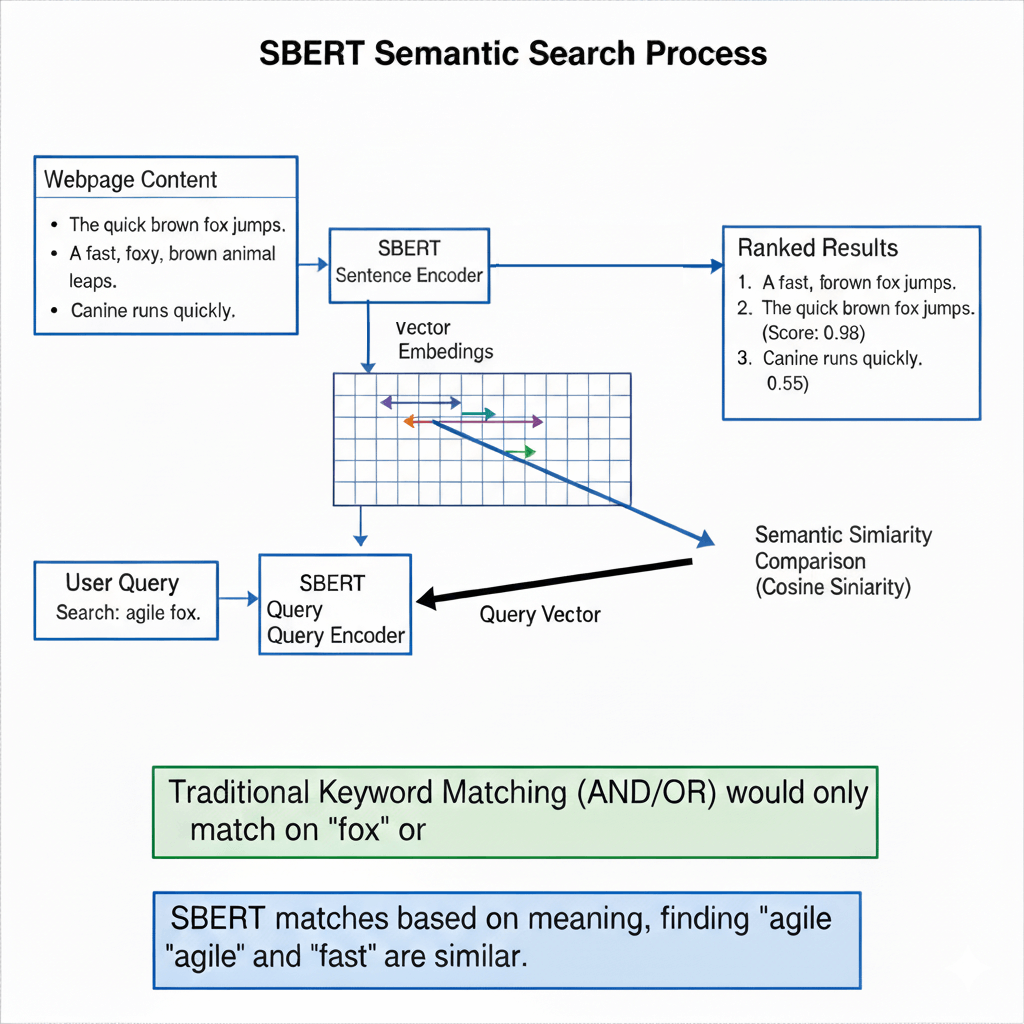
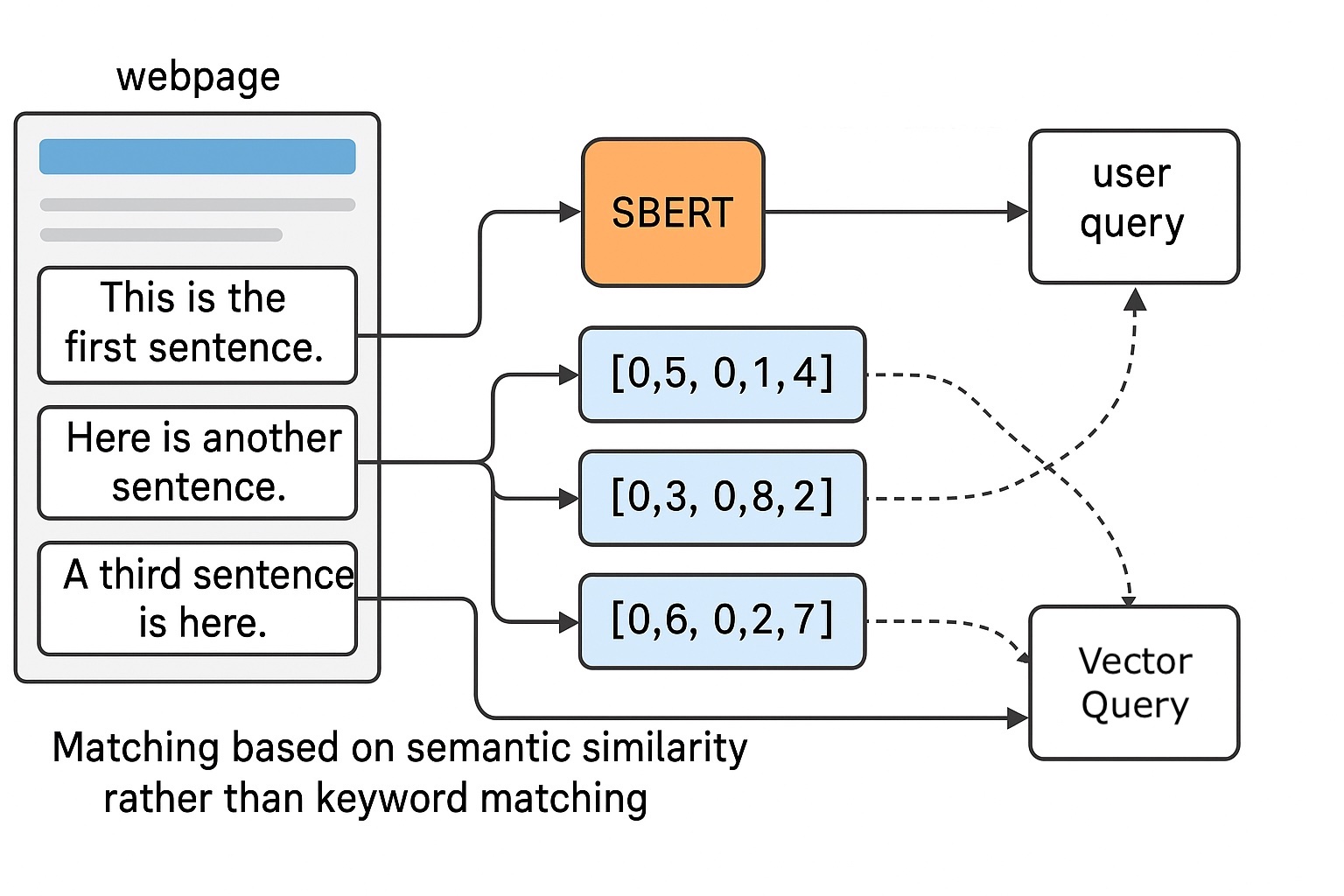
The difference extends to how search engines process information. Google’s Sentence-BERT (SBERT) model, which underlies much of its semantic understanding, evaluates content at the sentence and paragraph level rather than just counting keyword frequency. SBERT creates dense vector representations of text that capture semantic meaning, allowing the system to understand that “automotive paint supplier in Selangor” and “manufacturer of industrial coatings in Malaysia” might be describing the same type of business, even without shared keywords.
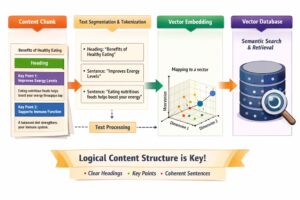
This means your content must be structured for extraction and comprehension, not just keyword density. Each section should clearly answer a specific question or explain a specific concept. Your paragraphs should work as standalone units of information that AI systems can confidently cite or reuse.
How Does AI SEO Relate To Google MUM And Modern Search Behaviour
Google MUM (Multitask Unified Model) represents a significant leap in how search engines understand and process information. Unlike previous updates that improved specific aspects of search, MUM was designed to handle multiple tasks simultaneously across different formats and languages.
To understand MUM’s impact on Malaysian SEO, consider what “multitask unified model” actually means in practice. MUM can simultaneously understand text, images, and potentially video content. It can comprehend queries in one language and retrieve relevant information in another. Most importantly for Malaysian businesses, it can understand complex, multi-faceted questions that previously would have required several separate searches.
Imagine a Malaysian family planning a trip to Sabah. They might search: “hiking di Kinabalu in November, sesuai tak untuk kanak-kanak, apa perlu bawa”. This query mixes Malay and English, asks multiple questions (weather suitability, child-friendliness, packing requirements), and implies several underlying concerns (safety, difficulty level, temperature).
Traditional keyword-based SEO would struggle with this query. Which language should you optimize for? Which question is primary? MUM processes this as a unified intent: a family needs comprehensive hiking information that addresses safety, seasonality, and preparation, all specific to Kinabalu in November.
For Malaysian websites, this multilingual understanding is particularly powerful. If your website has comprehensive information about Kinabalu hiking in English, and another section discusses child-friendly activities in Bahasa Malaysia, MUM can connect these separate pieces of content to answer the compound query. The system understands that “kanak-kanak” and “children” refer to the same concept, that “November” relates to monsoon seasons, and that “apa perlu bawa” is asking about equipment recommendations.
MUM builds on earlier models like BERT but adds multimodal understanding. Where BERT excelled at understanding the relationship between words in a sentence, MUM understands the relationship between concepts across content types and languages. This aligns with how Malaysians actually search, often mixing languages, using voice search, or searching directly within platforms like TikTok or Instagram.
Modern Malaysian search behaviour shows several patterns that make AI SEO particularly relevant. Mobile usage dominates, with Malaysians frequently using voice search in mixed languages. Social media platforms function as search engines, especially for younger demographics who search TikTok for product reviews or restaurant recommendations. Local intent is pervasive, with queries constantly including location modifiers: “near me”, “di KL”, “dekat Johor Bahru”.
AI systems excel at understanding these local, conversational, multi-language queries because they process language as interconnected concepts rather than isolated keywords. Your job as a website owner is to ensure your content provides clear, comprehensive answers to these natural language questions.
What Does It Mean For A Website To Be “AI Ready” In Practical Terms
An AI ready website is one that AI systems can easily crawl, understand, parse into meaningful segments, and confidently cite or reuse when generating answers. This readiness operates at multiple levels: technical structure, content organization, entity clarity, and trust signals.
At the technical level, AI readiness starts with clean HTML structure and logical content hierarchy. AI systems parse your page by identifying distinct content blocks, typically using heading tags (H1, H2, H3) as primary signals. Each heading should introduce one clear concept or answer one specific question. The content under that heading should directly address the topic, starting with a concise answer followed by supporting details.
Consider a typical service page for a Malaysian accounting firm. An AI-ready version would structure content like this:
What Accounting Services Do We Provide in Malaysia?
[Direct answer paragraph listing core services: bookkeeping, tax filing, audit preparation, payroll management]
Who Are Our Accounting Services For?
[Clear paragraph identifying target clients: SMEs, startups, foreign companies setting up in Malaysia]
How Much Do Accounting Services Cost in Malaysia?
[Transparent pricing information or at least pricing ranges and factors that affect cost]
Each section answers a specific question with a direct, extractable answer. AI systems can pull the paragraph under “What Accounting Services” to answer one query, and pull from “How Much Do” to answer a pricing question, without needing to process the entire page.
Entity clarity is equally critical. Search engines build knowledge graphs, vast networks of entities (people, places, businesses, concepts) and the relationships between them. For your business to appear in AI-generated answers, search engines need to clearly understand what entity you represent.
This means having dedicated pages that define your core entities: your company, your services, your locations, your key products. For a Malaysian automotive paint manufacturer, this would include:
- A clear About page establishing the company entity (name, founding date, ownership, certifications)
- Individual service pages for each product category (industrial coatings, automotive refinish, protective coatings)
- Location pages for facilities (Selangor manufacturing plant, Johor distribution center)
- Consistent naming across all platforms (website, Google Business Profile, directories, social media)
Schema markup acts as structured fuel for AI systems. While humans read your content and infer meaning, AI systems process schema markup as explicit, unambiguous data about what your page contains. For Malaysian businesses, priority schema types include:
Organization schema defining your business entity, contact information, logo, social profiles, and founding date.
LocalBusiness schema for companies with physical locations, including opening hours, service areas, accepted payment methods, and price range.
Service schema for each service you offer, including service type, provider, area served, and relevant details.
FAQPage schema for question and answer content, which directly feeds into featured snippets and AI answer generation.
Here’s a practical example for a Malaysian SME:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "LocalBusiness",
"name": "Pristine Automotive Coatings Sdn Bhd",
"description": "Industrial and automotive paint manufacturer in Malaysia",
"address": {
"@type": "PostalAddress",
"streetAddress": "23 Jalan Teknologi 3/6",
"addressLocality": "Kota Damansara",
"addressRegion": "Selangor",
"postalCode": "47810",
"addressCountry": "MY"
},
"areaServed": ["Malaysia", "Singapore", "Brunei"],
"telephone": "+60-3-6140-XXXX",
"priceRange": "$$",
"sameAs": [
"https://facebook.com/pristinecoatings",
"https://linkedin.com/company/pristine-coatings"
]
}Trust signals matter more in AI SEO than in traditional SEO because AI systems are more cautious about citing unreliable sources. Google’s search quality guidelines emphasize Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T). For Malaysian businesses, demonstrating these qualities means:
Real business verification: Display your SSM registration number, business address, contact phone number that actually answers. Link to your Google Business Profile that shows real customer reviews.
Relevant certifications: If you’re ISO certified, JAKIM halal certified, KKM registered, or have industry-specific accreditations, prominently display these with verification links where possible.
Customer proof: Case studies from real Malaysian clients, testimonials with company names (with permission), before-and-after examples, project galleries.
Consistent information: Your business name, address, phone number, and services should match exactly across your website, Google Business Profile, social media, and directory listings.

How Can Malaysian Businesses Use AI SEO To Attract More Qualified Leads
AI SEO fundamentally changes the lead generation equation by shifting focus from ranking for high-volume keywords to being cited in answer contexts. The leads that come through AI-powered search tend to be more qualified because AI systems match content to user intent with greater precision than traditional keyword matching.
Consider how a potential customer’s journey unfolds in an AI-powered search environment. Someone searching “how to incorporate a company in Malaysia as a foreigner” likely sees an AI-generated overview that synthesizes information from multiple sources. If your corporate services website provides clear, comprehensive information addressing specific concerns foreign entrepreneurs face, documentation requirements, timeline expectations, and cost breakdowns, AI systems can reference your content within that overview.
The critical difference: traditional SEO would have you competing for ranking position one through ten. AI SEO has you competing to be included and cited in the synthesized answer, which means you’re not just driving traffic, you’re building authority and trust before the click even happens.
Malaysian businesses can leverage AI SEO for lead generation through several specific strategies:
Question-led content architecture: Map your customer journey as a series of questions. A B2B software company might address: “What is cloud ERP?”, “How much does ERP cost in Malaysia?”, “Can ERP integrate with our existing accounting system?”, “How long does ERP implementation take?”. Each question becomes a content section optimized for extraction and citation.
Local context integration: AI systems understand location context better than traditional search. When someone searches for services “in KL” or “near Subang”, ensure your content explicitly mentions these locations, discusses local requirements or challenges, and includes area-served markup in your schema.
Conversational content for voice search: Malaysians increasingly use voice search, often in Bahasa Malaysia or mixed language queries. Create content that answers natural language questions: “boleh ke claim tax relief for medical insurance”, “how to renew SSM online”, “mana nak daftar syarikat paling cepat”.
Service differentiation through detailed answers: Instead of generic service descriptions, address specific scenarios your target customers face. An accounting firm might create sections like “Accounting for e-commerce businesses in Malaysia”, “Tax filing for Malaysians working overseas”, “Bookkeeping for F&B businesses with multiple outlets”. This specificity helps AI systems match your content to precise user needs.
Trust-building content that converts: Include verifiable information that builds confidence: client success stories with specific results, detailed explanations of your process, transparent pricing or pricing factors, credentials and team information, response time commitments. When AI systems cite your content, these trust signals transfer to the citation context.
The lead quality improvement comes from better intent matching. Traditional SEO might drive traffic from broad informational queries that rarely convert. AI-powered search tends to surface your content for specific, often transactional or commercial intent queries where the user is further along their decision journey.
A practical example: A Malaysian logistics company optimized for “freight forwarding services Malaysia” might get traffic from people just learning about freight forwarding. The same company optimizing for AI-ready content addressing “how to ship machinery from Malaysia to Indonesia”, “import duties for electronics into Malaysia”, “FCL vs LCL shipping cost comparison Malaysia” gets more qualified leads with specific needs.
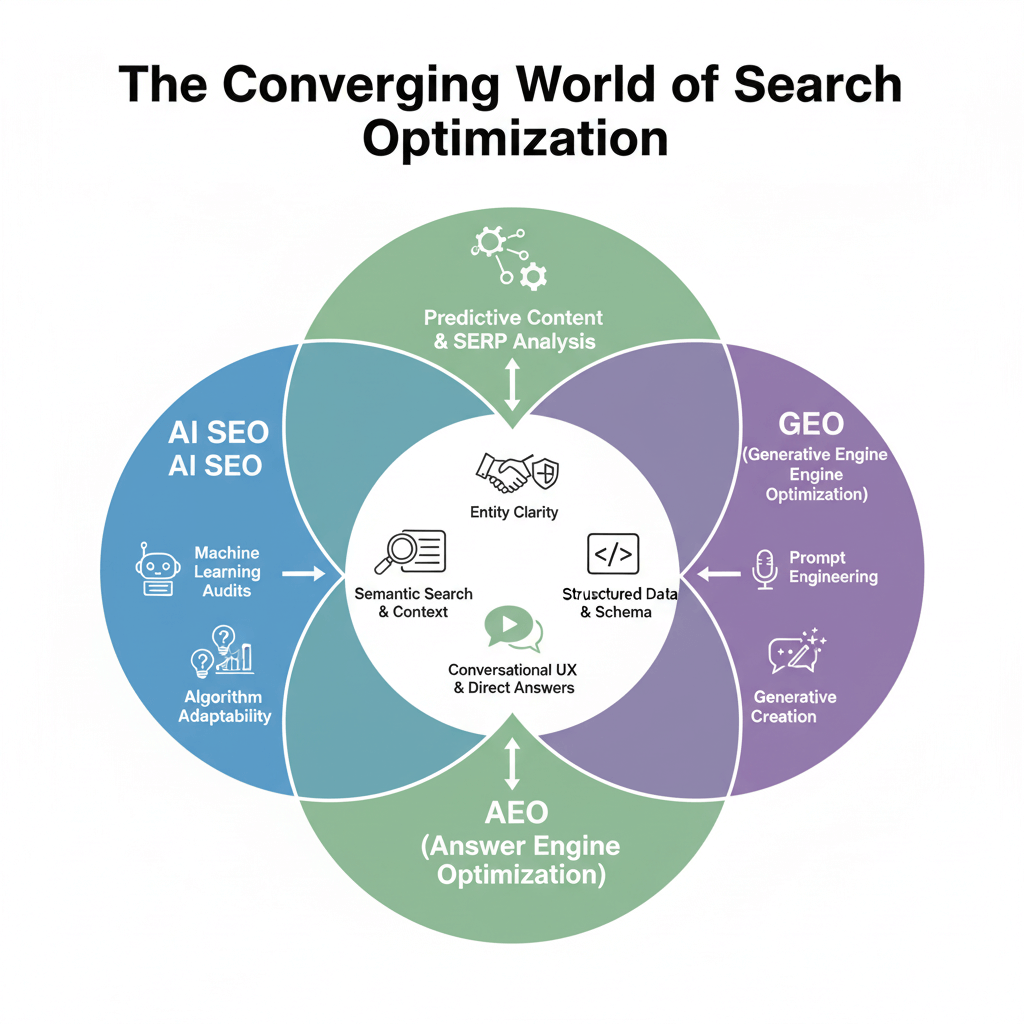
What Is The Difference Between AI SEO, AEO And GEO, And How Do They Work Together
The terminology around optimizing for AI-powered search can be confusing, with AI SEO, Answer Engine Optimization (AEO), and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) often used interchangeably. Understanding the distinctions helps clarify your optimization strategy.
AI SEO serves as the umbrella term covering the entire practice of optimizing for AI-powered search systems and using AI tools to improve your SEO workflow. It encompasses both the technical preparation of your website for AI comprehension and the strategic use of AI in content creation, keyword research, technical audits, and ongoing optimization.
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) focuses specifically on structuring content to be the best direct answer to explicit questions. AEO emerged from the rise of featured snippets, People Also Ask boxes, and voice search. The goal is to create content that search engines can confidently extract and present as a standalone answer.
AEO emphasizes:
- Question and answer format content
- Concise, direct answers followed by supporting information
- FAQ pages and sections
- Structured data that identifies questions and answers
- Optimization for featured snippet formats (paragraphs, lists, tables)
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) addresses the newer challenge of appearing in AI-generated overviews where systems synthesize information from multiple sources. Unlike traditional search where your page either ranks or doesn’t, or AEO where you either win the featured snippet or don’t, GEO involves being cited as one of several sources within a generated answer.
GEO focuses on:
- Being citeable and attributable (clear authorship, source credibility)
- Providing unique information or perspectives that add value to synthesized answers
- Comprehensive topical coverage so AI systems view you as an authoritative source
- Multi-step, conversational content that addresses follow-up questions
- Building relationships between related content pieces through internal linking
The overlap between these approaches is substantial. All three prioritize clear structure, entity clarity, trust signals, and comprehensive topic coverage. All three benefit from the same technical optimizations: clean HTML, proper schema markup, logical content hierarchy, fast page speed.
The key differences lie in scope and specific tactics:
AI SEO is the broadest, including workflow optimization (using AI tools for research, content generation, technical analysis) alongside content and technical optimization. It’s both the strategy and the toolset.
AEO is page-level optimization focused on question-answer matching. It’s about winning specific answer positions for specific queries. AEO is tactical and query-focused.
GEO is about building authority and citability across your domain so that AI systems view you as a reliable source worth including in synthesized answers. GEO is strategic and domain-focused.
For Malaysian businesses, here’s how they work together in practice:
Start with AI SEO as your framework. Use AI tools to identify questions your target audience asks, analyze competitor content gaps, and generate content outlines. Ensure your technical foundation is solid: fast loading, mobile optimized, clean structure, proper schema.
Apply AEO tactics to your money pages and core topic areas. For each primary service or product, create dedicated sections answering the five to ten most common questions. Structure these for featured snippet capture using concise answers, clear formatting, and FAQPage schema.
Build GEO into your content strategy. Instead of creating individual pages optimized for isolated keywords, build topic clusters where a pillar page covers a broad subject comprehensively, and supporting articles dive deep into specific aspects. Interlink these pieces to demonstrate topical authority. This cluster approach signals to AI systems that you’re a comprehensive resource worth citing across multiple related queries.
A Malaysian digital marketing agency might implement this integration:
- AI SEO foundation: Use AI tools to analyze 500+ search queries related to digital marketing in Malaysia. Identify question patterns, intent clusters, and content gaps. Implement proper technical setup with Organization and LocalBusiness schema.
- AEO for service pages: Create dedicated sections on each service page (SEO, PPC, Social Media Management) with FAQ schema addressing common questions: “How much does SEO cost in Malaysia?”, “How long before we see SEO results?”, “Do you work with small businesses?”.
GEO for thought leadership: Build topic clusters around core themes like “SEO for Malaysian SMEs”, “Social media marketing in Southeast Asia”, “PPC for e-commerce in Malaysia”. Each cluster has a comprehensive pillar page and 8-12 supporting articles that cover specific angles, case studies, and how-to guides. This establishes domain authority that makes AI systems more likely to cite you when answering related questions.
How Should I Structure My Pages And Content So AI Systems Can Understand And Reuse Them
Content structure for AI systems requires thinking in extractable blocks rather than flowing narratives. Each section of your page should function as a standalone unit that makes sense even when extracted from its original context.
The inverted pyramid approach: Start each section with the direct answer or core information, then provide supporting details, examples, and context. This mirrors how journalists write news stories and how AI systems prefer to process information. The first paragraph under each heading should be able to stand alone as a complete answer.
For a Malaysian property management company, a section might look like this:
H2: What Property Management Services Do We Offer in Kuala Lumpur?
[Direct answer paragraph]: We provide full-service property management for residential and commercial properties in Kuala Lumpur, including tenant screening, rent collection, maintenance coordination, legal compliance, and financial reporting. Our services cover condominiums, apartment buildings, office spaces, and retail properties.
[Supporting detail]: Our tenant screening process includes employment verification, credit checks, and reference validation to ensure reliable occupants. We handle all communication with tenants, from move-in procedures to handling maintenance requests and addressing concerns.
[Additional context]: Based in the heart of KL, we manage over 200 properties across areas including KLCC, Mont Kiara, Bangsar, and Damansara Heights. Our team understands local council regulations, strata management requirements, and the unique challenges of property management in Malaysian high-rises.
Notice how the first paragraph provides a complete, extractable answer. AI systems can confidently cite this paragraph because it’s comprehensive, specific, and self-contained. The supporting paragraphs add value for human readers while providing additional context for AI systems to assess relevance and authority.
Question-based heading structure: Frame your H2 and H3 headings as questions that real users ask. This directly aligns with how people search, especially in voice search and conversational AI interfaces. Use Search Console to identify question queries you already rank for, check People Also Ask boxes for related topics, and monitor Malaysian forums (Lowyat, Facebook groups, Reddit Malaysia) to capture authentic question phrasing.
Common question frameworks that work well:
- What is [topic] and why does it matter for Malaysian businesses?
- How to [accomplish task] in Malaysia [step-by-step guide]
- How much does [service] cost in Malaysia?
- What are the pros and cons of [option A] vs [option B]?
- Who should use [service] and when?
- Where can I [find/buy/access] [product/service] in [Malaysian location]?
Content block best practices for AI extraction:
- Keep paragraphs focused: Each paragraph should develop one idea. If you find yourself using “Additionally” or “Furthermore” multiple times in a paragraph, you’re probably combining multiple ideas that should be separate blocks.
- Use descriptive lists: When presenting multiple items, use HTML lists (ordered or unordered) with descriptive content for each point, not just short phrases. AI systems can extract list items as individual data points.
- Add TLDR or summary sections: For longer articles, include “Key Takeaways” or “Summary” sections that distill the main points into three to five clear statements. These become prime extraction targets for AI overviews.
- Incorporate comparison tables: For any “X vs Y” content, include properly marked-up HTML tables. AI systems excel at extracting tabular data and presenting it in answer formats.
- Use clear attribution: When citing statistics, research, or expert opinions, clearly attribute the source. AI systems favor content that demonstrates rigorous sourcing: “According to Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation, SMEs contribute 38% of GDP” is more citeable than “SMEs are important to Malaysia’s economy.”
Entity-driven content organization: Build your information architecture around your core entities. If you’re a Malaysian automotive supplier, your entity structure might include:
- Company entity page (About, history, facilities, certifications)
- Service entity pages (one for each major service category)
- Product entity pages (one for each product line or major product)
- Location entity pages (one for each physical location or major service area)
- Topic pillar pages (one for each major subject area you want to own)
Each entity page should thoroughly define that entity, its relationships to other entities, its attributes, and its value proposition. Link related entities to each other, creating a knowledge graph of your domain that mirrors how AI systems conceptualize information.
The before, during, after framework: For process or how-to content, structure information chronologically:
- Before: What you need to know, prepare, or have ready
- During: Step-by-step instructions for the main process
- After: What to do next, how to validate success, common follow-up questions
This framework naturally aligns with how AI systems answer process questions, making your content more extractable for “how to” queries.
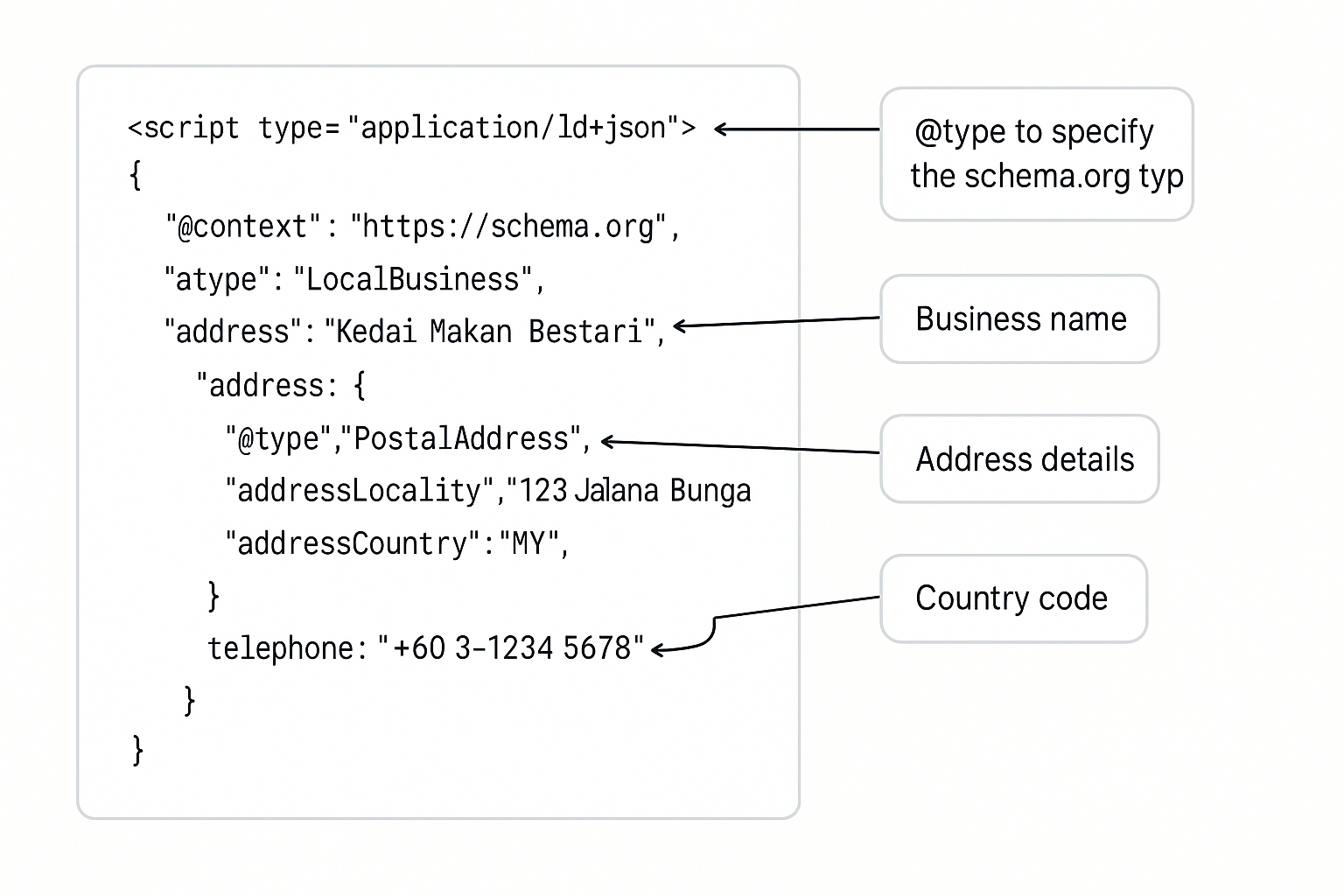
What Kind Of Schema Markup Should Malaysian Websites Prioritise For AI SEO
Schema markup acts as explicit metadata that tells AI systems exactly what your content means, removing ambiguity and improving the accuracy of content extraction. For Malaysian websites, schema priority depends on business type, but several schema types deliver universal value.
Organization schema should be implemented on every Malaysian business website, typically in the footer or header so it appears on every page. This schema establishes your business as a entity in Google’s knowledge graph.
Priority properties for Organization schema:
- name (official registered business name)
- alternateName (if you have a common shortened name or acronym)
- description (concise business description in 150-200 characters)
- url (your website homepage)
- logo (URL to your official logo image)
- telephone (main business contact number with country code)
- email (general inquiry or main business email)
- address (full postal address in PostalAddress schema)
- sameAs (array of URLs to your official social media profiles, business directories, LinkedIn company page)
- foundingDate (business establishment date)
LocalBusiness schema builds on Organization schema for businesses with physical locations serving local customers. This is critical for restaurants, retail stores, service providers, clinics, salons, and any business where customers visit a physical location.
Additional properties for LocalBusiness:
- priceRange ($ to $$$$ indicating general price level)
- openingHoursSpecification (detailed hours for each day)
- geo (GeoCoordinates for precise location)
- areaServed (cities or regions you serve)
- paymentAccepted (cash, credit card, online payment, etc.)
- acceptsReservations (boolean for booking availability)
For businesses with multiple locations (retail chains, franchise operations, service providers with branches), implement LocalBusiness schema uniquely for each location page with location-specific details.
Service schema defines individual services you offer, their attributes, and delivery areas. This is particularly valuable for service-based businesses: professional services (accounting, legal, consulting), home services (cleaning, renovation, maintenance), B2B services (logistics, IT services, training).
Key Service schema properties:
- name (service name)
- description (detailed service description)
- provider (reference to your Organization)
- areaServed (specific areas where you provide this service)
- serviceType (service category from relevant taxonomy)
- offers (Offer schema including price or price range if applicable)
Product schema for e-commerce sites, manufacturers, or distributors. Product schema is essential for appearing in product-related AI answers and Google Shopping surfaces.
Critical Product schema properties:
- name (product name)
- description (product description)
- image (high-quality product image)
- brand (your brand or manufacturer)
- sku (stock keeping unit)
- offers (including price, availability, seller, valid dates)
- aggregateRating (if you have product reviews)
- review (individual product reviews)
FAQPage schema is among the most valuable for AI SEO because it directly feeds featured snippets, People Also Ask boxes, and AI-generated answers. Implement FAQPage schema on pages with question-and-answer content.
Structure your FAQ schema with:
- mainEntity array containing Question objects
- Each Question has a name (the question text) and acceptedAnswer
- Each acceptedAnswer has text (the answer, which can include HTML for formatting)
Implement FAQPage schema on:
- Dedicated FAQ pages covering common questions about your business or industry
- Service pages with 3+ questions about that specific service
- Product pages with common customer questions
- Blog articles structured as questions with detailed answers
Article schema for blog posts, guides, news articles, and long-form content. Article schema helps AI systems understand content freshness, authorship, and subject matter.
Important Article schema properties:
- headline (article title)
- description (meta description or summary)
- image (featured image)
- author (Person or Organization schema)
- publisher (your Organization schema)
- datePublished and dateModified (ISO 8601 format)
- articleBody (full article text)
BreadcrumbList schema clarifies your site’s information hierarchy, helping AI systems understand how pages relate to each other and where specific content fits within your site structure.
VideoObject schema if you have video content on your pages. Video is increasingly important for multimodal AI systems like MUM that process both text and visual content.
Implementation priorities for Malaysian SMEs:
Start with:
- Organization schema (establishes your entity)
- LocalBusiness schema if applicable (connects you to local search)
- Service or Product schema for your top 5 offerings (defines what you do)
Add next: 4. FAQPage schema on money pages (captures question traffic) 5. BreadcrumbList schema (clarifies site structure)
Add when resources allow: 6. Article schema for blog content 7. Review/AggregateRating schema if you have reviews 8. VideoObject schema for video content
Technical implementation approaches:
JSON-LD format: The preferred method. Add schema as a JSON-LD script tag in your page head or body. This keeps schema separate from your visible HTML, making it easier to maintain and update.
WordPress plugins: If using WordPress, plugins like Rank Math, Yoast SEO Pro, or Schema Pro can generate schema automatically based on your content. Verify the output in Google’s Rich Results Test to ensure accuracy.
Manual JSON-LD templates: For custom sites, create JSON-LD templates for each page type (service page template, blog post template, location page template) that populate with dynamic content from your CMS.
Schema generators: Tools like Schema.org’s generator, Technical SEO‘s schema generator, or Merkle’s schema generator can help you create properly formatted JSON-LD code that you paste into your pages.
Quality assurance for schema:
- Test every schema implementation in Google’s Rich Results Test
- Use the Schema Markup Validator to check syntax
- Verify that dynamic content populates correctly in schema
- Ensure dates use ISO 8601 format (YYYY-MM-DD)
- Use complete URLs (including https://) for all URL properties
- Keep descriptions and text under recommended character limits
- Match information exactly between schema and visible page content
How Can Small Businesses With Limited Budget In Malaysia Start With AI SEO
Malaysian SMEs often operate with tight marketing budgets, limited technical resources, and small teams juggling multiple responsibilities. The good news: effective AI SEO doesn’t require expensive tools or large teams. It requires strategic focus and consistent execution.
Start with clarity before complexity: Before investing in tools or extensive content creation, gain absolute clarity on three foundations:
- Your entity: Who are you, what do you offer, and who is it for? Write a clear 200-word business description. List your five core services or product categories. Define your primary service areas geographically.
- Your customer questions: What do potential customers need to know before buying from you? What concerns or objections do they have? What mistakes do they want to avoid? List 20-30 actual questions your sales or customer service team hears repeatedly.
- Your differentiators: What makes you different from competitors? What unique value, experience, or approach do you bring? What results or outcomes have you delivered for Malaysian clients?
With these three elements clear, you have the foundation for AI-ready content.
Free and low-cost AI SEO workflow for Malaysian SMEs:
Research phase (free tools):
- Google Search Console to identify questions you already rank for
- Google’s “People Also Ask” boxes for related question discovery
- Answer The Public (limited free searches) for question variations
- ChatGPT free tier to cluster questions into themes
- Reddit Malaysia, Lowyat forums, relevant Facebook groups to find authentic Malaysian phrasing of questions
Content creation (free tools plus your time):
- Use ChatGPT or Claude to generate content outlines based on your question list
- Write first drafts yourself or have your team member who knows the topic best write them
- Use AI to expand sections, add examples, or rewrite for clarity
- Never publish AI-generated content without human review, editing, and adding specific examples from your business
Technical implementation (free to low-cost):
- If using WordPress: Rank Math free version provides excellent schema markup and technical SEO features
- For custom sites: Use free schema generators to create JSON-LD, then paste into your template
- Google’s Rich Results Test (free) to verify schema
- PageSpeed Insights (free) to check page speed
- Mobile-Friendly Test (free) to ensure mobile optimization
Ongoing optimization (free monitoring):
- Set up Google Search Console and check monthly for new question queries
- Google yourself and your key services to see if you appear in AI overviews or featured snippets
- Search your brand name in ChatGPT and Perplexity to check if you’re being cited
- Track rankings for your top 10 question-based queries using free rank trackers (limited checks per day)
Practical AI SEO workflow for one service page (2-4 hours total):
- Research (30 minutes): Use Search Console and People Also Ask to identify 5-10 questions related to this service. Check what competitors cover. Note any questions they miss.
- Structure (15 minutes): Create an outline with H2s for each main question. Under each H2, plan for a direct answer paragraph plus supporting details.
- Write (60-90 minutes): Write (or have AI draft then heavily edit) the page content. Focus first on clear, direct answers. Add supporting details and examples second. Include 2-3 customer testimonials or case study snippets.
- Schema (30 minutes): Generate Organization and Service schema using a free tool. If you have 3+ FAQs, add FAQPage schema. Implement the JSON-LD on your page.
- Quality check (15 minutes): Read the page aloud to ensure it sounds natural. Verify all links work. Test schema in Rich Results Test. Check mobile display.
- Monitor (10 minutes monthly): Check Search Console for impressions and clicks. Google the main question to see if you appear in results or AI overviews.
Priority order for limited resources:
If you can only optimize five pages this year:
- Homepage (establish entity with Organization schema)
- Top-revenue service page (full question-based structure with Service and FAQPage schema)
- Your most common customer inquiry topic (comprehensive answer to main question plus related questions)
- Local landing page for your main service area (LocalBusiness schema)
- About page (establish trust with company background, team, certifications)
What to avoid when budget is limited:
Don’t: Pay for expensive content creation services that mass-produce AI-generated articles without strategyor quality control. This creates more problems than value.
Do: Write fewer pieces yourself or with your team, ensuring each piece thoroughly addresses real customer questions with specific, accurate information.
Don’t: Buy complex schema plugins or tools if you don’t understand what schema does or why you need it.
Do: Start with free schema generators and basic implementations. Add complexity only after you understand the basics and see results.
Don’t: Try to rank for high-competition broad keywords just because they have high search volume.
Do: Focus on specific, long-tail questions where you can provide uniquely valuable answers. “How to choose accounting software for Malaysian restaurant business” is more achievable and valuable than “accounting software Malaysia”.
Don’t: Create content in only one language if your customers speak multiple languages.
Do: Ensure key pages exist in both English and Bahasa Malaysia if your audience includes both language groups. Quality translations matter more than quantity of pages.
Building momentum over time:
Month 1-2: Establish foundation. Implement Organization schema. Optimize homepage and top service page with question structure and schema.
Month 3-4: Add depth. Create FAQ page addressing 15-20 common questions. Add FAQPage schema. Optimize second-priority service page.
Month 5-6: Build authority. Write first blog article thoroughly covering a topic your customers ask about frequently. Optimize local landing page with LocalBusiness schema.
Month 7-12: Expand systematically. Add one optimized service page or comprehensive blog article per month. Monitor what’s working in Search Console and double down on those topics.
The constraint of limited budget actually helps maintain focus. Large companies with big budgets often create hundreds of mediocre AI-generated pages that add little value. Small businesses that create 10-20 excellent, AI-ready pages addressing real customer needs often see better results because each page receives proper attention and provides genuine value.
What Tools Are Useful For AI SEO And Which Ones Are Realistic For Malaysian SMEs And Agencies
The AI SEO tool landscape ranges from free options to enterprise platforms costing thousands of dollars monthly. For Malaysian businesses, the challenge isn’t finding tools but choosing the right tools for your specific needs and budget level.
Research and topic mapping tools:
Free tier / low cost:
- Google Search Console: Essential for every website. Shows what questions you already rank for, which pages get traffic, and technical issues.
- Google Keyword Planner: Free with Google Ads account (no spending required). Basic search volume data for Malaysia.
- Answer The Public: Limited free searches show question variations around your keywords.
- ChatGPT free tier: Excellent for clustering questions into themes, generating content outlines, and finding semantic variations of topics.
- AlsoAsked.com: Free daily searches show People Also Ask relationships for questions.
Mid-range (suitable for agencies and growing SMEs):
- Ahrefs ($99-$179/month): Comprehensive keyword research, content gap analysis, SERP analysis. Their “Questions” filter specifically identifies question-based queries.
- SEMrush ($119-$229/month): Similar to Ahrefs with strong keyword research and position tracking. Topic Research tool helps identify question clusters.
- Keywords Everywhere (browser extension, $10-$100 one-time credit purchase): Shows search volume and related keywords directly in Google search results.
For Malaysian context: Most international tools show limited or no data for Bahasa Malaysia keywords. Use Google Keyword Planner for BM keywords as it has the most complete Malaysian data. Combine with manual research in Malaysian forums and social media.
Content creation and optimization tools:
Free to low cost:
- ChatGPT (free or $20/month for Plus): Generate outlines, expand sections, rewrite for clarity, create FAQ lists, translate between English and Bahasa Malaysia.
- Claude (free tier available): Excellent for longer-form content analysis and editing. Good at maintaining context across long conversations.
- Grammarly (free tier): Basic grammar and clarity checking for English content.
- Hemingway Editor (free web version): Ensures content is readable and clear.
Mid-range:
- Surfer SEO ($69-$199/month): Analyzes top-ranking pages and provides content recommendations. Content Editor scores your content in real-time.
- Clearscope ($170+/month): Topic modeling and content optimization. Good for ensuring comprehensive coverage.
- Frase ($15-$115/month): Combines research, outlining, and optimization. Good value for agencies managing multiple clients.
Agency tier:
- MarketMuse ($149+/month): Advanced topic modeling and content planning. Better suited for larger content operations.
Schema and technical implementation tools:
Free:
- Google’s Rich Results Test: Essential for validating schema markup.
- Schema Markup Generator by Merkle: Creates valid JSON-LD for common schema types.
- Screaming Frog (free up to 500 URLs): Technical SEO crawler showing structure, metadata, and some schema issues.
WordPress users:
- Rank Math (free or $59/year pro): Excellent schema implementation, technical SEO features, and clean interface. Best value for WordPress users.
- Yoast SEO (free or $99/year premium): Widely used, good support, but schema features less comprehensive than Rank Math in free tier.
- Schema Pro ($79/year): Dedicated schema plugin if you need more schema types than general SEO plugins provide.
Paid technical tools:
- Screaming Frog ($209/year for unlimited URLs): Industry standard for technical audits.
- Sitebulb ($35-$165/month): Visual crawling reports excellent for client presentations.
Monitoring and tracking tools:
Free:
- Google Search Console: Track rankings, impressions, featured snippet appearances.
- Manual SERP checking: Search your target questions in incognito mode across different devices to see if you appear in AI overviews or featured snippets.
- Perplexity and ChatGPT: Search your brand and key topics to see if you’re being cited.
Paid:
- AccuRanker ($109+/month): Fast, accurate rank tracking. Good for agencies tracking many keywords across multiple clients.
- SE Ranking ($44-$176/month): Affordable all-in-one with rank tracking, site audits, and competitor analysis. Good value for Malaysian agencies.
- Advanced Web Ranking ($49-$149/month): Detailed local rank tracking useful for multi-location businesses.
Recommended tool stack for Malaysian SMEs:
Minimum viable stack (under $50/month):
- Google Search Console (free)
- ChatGPT Plus ($20/month)
- Rank Math free (if WordPress)
- Manual schema implementation with free generators
- Manual SERP and AI overview monitoring Total: $20/month
Growing business stack ($100-150/month):
- Google Search Console (free)
- ChatGPT Plus or similar AI assistant ($20/month)
- Ahrefs Lite or SEMrush Pro ($99-119/month)
- Rank Math Pro for WordPress or paid schema tool for custom sites ($59-99/year)
- Basic rank tracker or manual tracking Total: $120-140/month
Agency stack ($300-500/month for managing 5-10 clients):
- Google Search Console (free)
- ChatGPT or Claude Plus ($20-40/month)
- Ahrefs or SEMrush Standard ($179-229/month)
- Rank Math Pro or Schema Pro for clients ($79-99/year)
- SE Ranking or AccuRanker ($109+/month)
- Screaming Frog paid license ($209/year) Total: $320-400/month plus annual tool costs
Tool usage best practices:
Don’t rely solely on AI writing tools: Use them for outlines, expansion of ideas, and rewriting for clarity. Always add specific examples, local context, and authentic insights that only you or your team can provide.
Combine tools strategically: Use Ahrefs or SEMrush for research and gap analysis, ChatGPT for content outlining and question clustering, then human expertise for writing and optimization.
Focus on free data sources first: Before paying for tools, extract maximum value from Search Console, People Also Ask, customer conversations, and sales team insights.
Validate tool recommendations: If an AI tool or SEO platform suggests changes, understand why before implementing. Tools can suggest adding keywords or topics that aren’t actually relevant to your business.
Track tool ROI: Every three months, review whether paid tools are actually being used and contributing to results. Tools you don’t use regularly should be cancelled.
The right tool stack evolves with your needs. Start minimal, prove value, then add tools as specific needs emerge. A Malaysian SME generating RM500,000 in annual revenue might only need $20/month in tools. An agency managing 10 clients with RM3 million in billings can justify $500/month in tools that improve efficiency and results.
How Do I Measure Whether My AI SEO Efforts Are Working, Beyond Just Rankings
Traditional SEO success metrics focused heavily on keyword rankings and organic traffic. AI SEO requires broader measurement because success isn’t just about ranking position one but about being cited, appearing in AI overviews, winning featured snippets, and building brand authority that influences purchase decisions even before users visit your site.
AI visibility metrics (primary indicators):
Featured snippet appearances: Track how many keywords trigger featured snippets where your content appears. Check Search Console’s “Search Appearance” filter for featured snippet impressions. Featured snippets in AI SEO matter because they often seed AI-generated overviews.
People Also Ask (PAA) appearances: Monitor whether your content appears in PAA boxes for your target questions. Use tools like AlsoAsked or manual tracking by searching target keywords and checking PAA results.
AI overview citations: Google increasingly shows AI-generated overviews above traditional results. Check whether your site is cited as a source in these overviews for your target topics. Currently, this requires manual checking as few tools track this consistently.
Zero-click search frequency: Track queries where your content appears in featured snippets or AI overviews but generates fewer clicks than expected. This seems negative but actually indicates your content is valuable enough to answer questions directly. If you’re building brand awareness and authority, zero-click appearances still provide value.
How to track AI visibility manually:
Create a spreadsheet listing your 20-30 priority questions or topics. Once per month:
- Search each question in incognito mode on desktop and mobile
- Note whether you appear in: traditional results (and position), featured snippets, PAA boxes, AI overviews
- Screenshot appearances for reporting purposes
- Track changes over time
Entity and brand awareness metrics:
Brand search volume: Track searches for your company name, product names, or unique service names. Growing brand search indicates improving awareness from AI surface appearances.
Brand mention tracking: Monitor whether AI systems (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude) mention your brand when asked about your industry or service category. Example: “What are reputable accounting firms in Kuala Lumpur?”
Knowledge Graph presence: Check whether Google shows a Knowledge Panel for your brand. This indicates strong entity recognition. For local businesses, Google Business Profile prominence serves a similar role.
Traffic and engagement quality metrics:
Question-based query traffic: In Search Console, filter for queries containing “what”, “how”, “why”, “when”, “where”. Track growth in impressions and clicks from question queries versus standard keyword queries.
Content engagement depth: Track average time on page and scroll depth for your AI-optimized pages. Visitors from AI surfaces often arrive with specific intent, leading to higher engagement if your content delivers on the promise.
Conversion rate by traffic source: Compare conversion rates from different query types. Question-based traffic and featured snippet traffic often convert differently than traditional keyword traffic. Track which performs better for your specific goals.
Page-level performance metrics:
Impressions for target questions: For each AI-optimized page, track total impressions in Search Console for the specific questions you’re targeting.
Average position trends: While absolute ranking matters less in AI SEO, tracking whether you’re moving up or down the results page indicates competitive position.
Rich result eligibility: Track how many pages have valid schema that makes them eligible for rich results. Use Search Console’s “Enhancements” section to monitor schema validation.
Practical measurement framework for Malaysian SMEs:
Monthly dashboard (30 minutes to compile):
- Featured snippet count (from Search Console filter)
- Total impressions for question queries (filter Search Console for what/how/why/when/where queries)
- Top 10 questions driving traffic (Search Console query analysis)
- Organic traffic to AI-optimized pages (from Analytics)
- Conversion rate from organic search overall (from Analytics)
Quarterly deep dive (2-3 hours):
- Manual check of AI visibility for your 20 core questions
- Brand mention audit in AI systems (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI overview)
- Schema validation check for all priority pages
- Content performance review (which topics drive most engagement and conversions)
- Competitor analysis (are competitors appearing in AI surfaces where you’re not?)
Setting realistic expectations:
Timeline for results:
- Technical improvements (schema, site structure): 2-4 weeks for search engines to recrawl and reprocess
- Content optimization (question structure, clear answers): 4-8 weeks to see featured snippet or PAA appearances
- New content: 8-12 weeks for new pages to gain traction, longer for competitive topics
- Entity recognition: 3-6 months of consistent optimization and external validation (citations, reviews, directory listings)
What “good” looks like:
For a Malaysian SME with 20 optimized pages:
- 5-10 featured snippet appearances
- 20-30 PAA appearances
- 15-25% of organic traffic from question-based queries
- 2-3 mentions in AI system responses about your industry/category
For a Malaysian agency or larger business with 100+ optimized pages:
- 30-50 featured snippet appearances
- 100+ PAA appearances
- 30-40% of organic traffic from question-based queries
- Consistent appearances in AI overviews for core topics
- Knowledge Graph presence
Measuring beyond digital metrics:
Sales conversation quality: Are sales calls starting further along the buyer journey? Are prospects asking more informed questions? This indicates AI surfaces are pre-educating customers.
Repeat vs. new customer mix: Improved brand awareness from AI visibility often increases direct traffic and repeat business over time.
Customer testimonial quality: Are customers mentioning finding you through helpful content or answers to their questions? This qualitative feedback validates AI SEO impact.
The shift from traditional ranking metrics to AI visibility metrics requires educating stakeholders about what success looks like. A position five ranking that includes a featured snippet appearance often delivers more value than a position one ranking without snippet enhancement. A page that answers questions so well it generates zero-click searches can still build brand authority that drives conversions elsewhere in the customer journey.
What Are The Most Common AI SEO Mistakes That Malaysian Sites Make And How Can I Avoid Them
After auditing dozens of Malaysian websites for AI readiness, several mistakes appear repeatedly, often undermining otherwise solid SEO foundations. Recognizing these pitfalls helps you avoid wasting time and resources on approaches that won’t deliver results.
Mistake 1: Over-generating AI content without strategy or quality control
The availability of ChatGPT and similar tools has led many Malaysian businesses to produce massive volumes of AI-generated content with minimal editing or strategic planning. The result: dozens or hundreds of thin, generic pages that fail to rank and certainly don’t get cited by AI systems.
Why this fails: AI systems favor content that demonstrates expertise, provides unique insights, and thoroughly addresses user needs. Generic AI-generated content typically lacks specific examples, local context, and authentic expertise. Search engines can identify patterns of low-quality AI content, and the abundance of such content dilutes your site’s authority.
How to avoid: Use AI as a research and outlining tool, not a content replacement. Generate outlines with AI, identify topic gaps, draft preliminary structures, then have humans who actually understand the topic write and refine the content. Add specific examples from your business, local Malaysian context, customer case studies, and authentic insights that only you can provide. Quality matters far more than quantity.
Mistake 2: Ignoring local context and Bahasa Malaysia optimization
Many Malaysian websites optimize exclusively in English, even when serving a customer base that searches in Bahasa Malaysia or mixes languages. Others create BM pages as direct translations without considering how Malaysians actually search in Malay.
Why this fails: Google MUM and other AI systems excel at understanding multi-language contexts. Malaysians frequently search in BM, mix languages in queries (“insurance kereta murah”), or use localized English (“lawyer in PJ”, “clinic near Ampang”). Ignoring these patterns means missing a significant portion of search intent.
How to avoid: Research how your customers actually search in both English and Bahasa Malaysia. Use Google Keyword Planner for BM keyword volume. Monitor social media and forums to see authentic language usage. Create content in both languages when your audience is mixed, but ensure BM content addresses Malaysian-specific phrasing and concerns rather than serving as direct translations. Include location-specific content addressing areas your customers care about: “selayang”, “subang jaya”, “johor bahru”, not just generic “Malaysia” optimization.
Mistake 3: No schema markup or broken schema implementation
Many Malaysian websites either have no schema markup or have improperly implemented schema that fails validation, rendering it useless for AI systems.
Why this fails: Schema provides explicit, structured data about your content. Without it, AI systems must infer meaning from your HTML and text, increasing the chance of misinterpretation. Broken schema is worse than no schema because it signals poor technical quality to search engines.
How to avoid: Start with basic Organization and LocalBusiness schema on every site. Validate all schema using Google’s Rich Results Test before deploying. If using WordPress, use reliable plugins like Rank Math that generate valid schema automatically. For custom sites, use tested JSON-LD templates and validate each implementation. Check Search Console’s “Enhancements” section monthly for schema errors and fix them promptly.
Mistake 4: Thin service pages with no clear questions or value
Many Malaysian business websites have service pages that are essentially brochures: “We provide X service. Contact us for more information.” These pages fail to address customer questions, concerns, or decision criteria.
Why this fails: AI systems prioritize content that provides comprehensive, helpful information. A page that essentially says “we do accounting services, call us” offers nothing worth citing. Meanwhile, competitors who thoroughly explain accounting service options, pricing considerations, documentation requirements, and typical timelines become the go-to source for AI-generated answers.
How to avoid: Transform each service page into a comprehensive resource. Include sections addressing: what the service is, who it’s for, how it works, what it costs (or factors affecting cost), how to choose a provider, what to expect, common mistakes to avoid, and frequently asked questions. Add customer case studies or success stories. Provide enough information that a potential customer feels informed and confident, even before contacting you.
Mistake 5: Focusing only on tools instead of user value and business model alignment
Some Malaysian businesses invest heavily in AI SEO tools while neglecting the fundamental question: does our AI SEO strategy align with how we actually make money and serve customers?
Why this fails: You can rank for hundreds of questions that never convert to customers. You can appear in dozens of AI overviews for topics tangential to your business. Tools and tactics without strategy waste resources on visibility that doesn’t drive business value.
How to avoid: Start with your business model. How do you acquire customers? What information do they need at each stage? What questions, when answered, move prospects closer to purchasing? Build your AI SEO strategy around these high-value questions and topics. Measure success by qualified leads and customers, not just traffic or rankings. Ensure every piece of content you optimize serves a clear role in the customer journey.
Mistake 6: Inconsistent entity information across platforms
Malaysian businesses often have different versions of their name, address, phone number, or service descriptions across their website, Google Business Profile, Facebook page, and directory listings.
Why this fails: AI systems build entity understanding by connecting information across sources. Inconsistent entity data confuses these systems, reducing confidence in citing you as an authoritative source. It also dilutes local SEO signals critical for “near me” and location-based searches.
How to avoid: Create a master document with your official entity information: exact business name, full address, primary phone number, business categories, service descriptions, and social media URLs. Ensure this information appears identically across your website schema, Google Business Profile, major directories (Bing Places, Apple Maps), and social media profiles. When you update any information, update it everywhere simultaneously.
Mistake 7: Creating isolated content without topical clusters or internal linking
Many Malaysian websites create individual blog posts or pages without connecting them to related content, missing the opportunity to demonstrate topical authority.
Why this fails: AI systems assess whether a website is authoritative on a topic by evaluating comprehensive coverage. Individual isolated pages signal surface-level knowledge. Interconnected content clusters demonstrate depth and breadth of expertise, making AI systems more likely to cite you as an authoritative source.
How to avoid: Plan content in clusters around your core topics. For each major topic, create a comprehensive pillar page covering the subject broadly. Then create 8-12 supporting articles diving deep into specific aspects. Link related articles to each other and back to the pillar page. This structure signals topical authority and helps AI systems understand your domain expertise.
Mistake 8: Neglecting E-E-A-T signals and trust building
Many Malaysian SME websites lack basic trust signals: no team information, no physical address, no certifications displayed, no customer reviews or case studies.
Why this fails: AI systems are cautious about citing sources that lack credibility signals. In uncertain times with misinformation concerns, search engines prioritize content from trustworthy sources. Lack of trust signals means AI systems will cite competitors instead.
How to avoid: Display clear contact information including physical address and phone number on every page. Create an About page with team information and company background. Showcase relevant certifications (ISO, JAKIM, industry associations, professional qualifications). Collect and display customer testimonials and reviews. Link to your verified Google Business Profile. Include author information on blog articles. All of these signals help AI systems assess your trustworthiness.
Mistake 9: Expecting immediate results and abandoning strategy too quickly
Some Malaysian businesses implement AI SEO improvements, see no immediate ranking jumps after two weeks, and conclude AI SEO doesn’t work.
Why this fails: AI SEO results take time. Search engines need to recrawl your pages, process your schema, evaluate your content quality, and compare you against competitors. Entity recognition and topical authority build gradually. Expecting instant results leads to premature strategy abandonment before optimization has time to work.
How to avoid: Set realistic timeline expectations: 2-4 weeks for technical changes to be processed, 6-12 weeks for content optimizations to show results, 3-6 months for entity recognition to strengthen. Track leading indicators (featured snippet appearances, PAA inclusions, impressions growth) rather than only lagging indicators (traffic, conversions). Give your strategy at least six months before major course corrections.
Mistake 10: Optimizing for AI systems instead of humans
Some websites become so focused on structure, schema, and AI optimization that content becomes stilted, repetitive, or awkwardly formatted for actual human readers.
Why this fails: The ultimate goal of AI systems is satisfying user needs. Content optimized for AI extraction but poor for human readers will underperform because users bounce quickly, don’t engage deeply, and don’t convert. User experience signals feed back into AI system quality assessments.
How to avoid: Always optimize for humans first, AI systems second. Write naturally. Include personality and brand voice. Format for easy scanning and reading. While structure helps AI extraction, that structure should enhance rather than hinder human readability. Test your content with actual customers or colleagues: if they find it awkward or robotic, rewrite until it flows naturally while maintaining the structural elements AI systems need.
By avoiding these common mistakes, Malaysian businesses position themselves to benefit from AI-powered search rather than being left behind by competitors who implement AI SEO more effectively.
How Can Agencies Explain AI SEO Benefits To Malaysian Clients Who Are Not Technical
Explaining AI SEO to non-technical Malaysian clients requires translating complex technical concepts into business outcomes they care about: more qualified leads, stronger brand recognition, higher conversion rates, and sustainable competitive advantage.
Start with the problem, not the solution:
Don’t begin with: “We need to implement JSON-LD schema markup using Organization and LocalBusiness schema types to improve entity recognition in Google’s knowledge graph.”
Instead begin with: “When potential customers in KL search for [your service], they’re seeing AI-generated answers that mention your competitors but not your company. We need to fix this so your business appears in these answers and gets the visibility you deserve.”
Frame AI SEO in terms of the client’s pain points: losing leads to competitors, not appearing in modern search results, customers going to competitors because they look more credible online, spending on digital marketing without clear returns.
Use concrete before-and-after examples:
Abstract explanations rarely resonate. Show specific examples:
Before AI SEO: “When someone searches ‘best accounting firm for SME in Malaysia’, here’s what they see. [Show screenshot]. Notice how our competitors appear in the AI overview but your firm doesn’t. This means potential customers are learning about competitors before they even visit any website.”
After AI SEO: “After we optimize your content and technical setup, when someone searches that same question, here’s what they see. [Show mockup or example from another client]. Your firm now appears as one of the cited sources. Customers are reading about your services before they visit any website. This builds trust and makes them more likely to choose you when they’re ready to contact an accountant.”
Visual proof makes the concept immediately tangible.
Explain in terms of customer journey changes:
“Think about how you find information now versus five years ago. You probably ask Google or ChatGPT questions and expect direct answers, not a list of websites to click through. Your customers do the same. AI SEO ensures your business information appears in these direct answers, meeting customers where they actually search.”
Connect to their personal experience. Most Malaysian business owners have used ChatGPT or seen Google’s AI overviews. Helping them recognize they’re already experiencing AI-powered search makes the concept immediately relevant.
Focus on competitive advantage:
“Your competitors aren’t doing this yet. Most Malaysian businesses are still optimizing the old way, targeting keywords but not structuring content for AI. This is your window to get ahead. In 6-12 months, everyone will be doing AI SEO. Right now, you can be the first in your industry to appear consistently in AI answers.”
Business owners respond to competitive positioning. If their competitors aren’t yet visible in AI surfaces but could be, that’s a threat. If they can become visible first, that’s an opportunity.
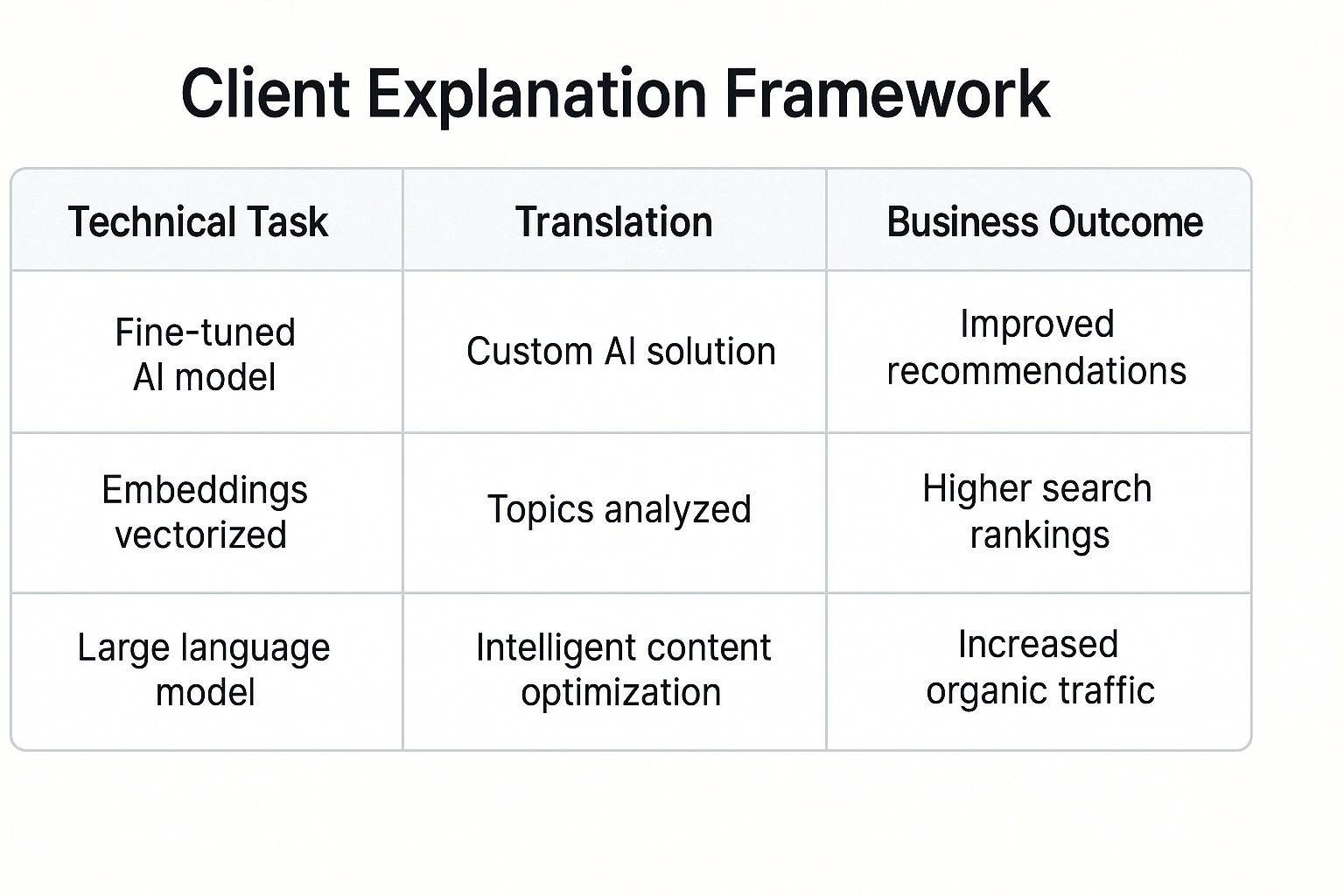
Translate technical work into business outcomes:
Instead of listing technical tasks, frame deliverables as outcomes:
Technical framing (what not to say): “We’ll implement Organization schema with sameAs and areaServed properties, create FAQPage schema for your service pages, optimize your heading structure for semantic chunking, and build topical authority clusters around your money keywords.”
Business outcome framing (what to say): “We’ll make sure Google understands exactly what services you offer and where you serve, so you appear in local searches. We’ll structure your service pages to answer the exact questions your customers ask, increasing the chances your business gets featured in answer boxes. We’ll create a series of helpful articles that establish you as the go-to expert in your field, making Google more likely to recommend you.”
Every technical task should map to a clear business benefit.
Use simple analogies:
“Think of AI SEO like organizing a library. Traditional SEO was like putting your book on the shelf and hoping people find it. AI SEO is like having a librarian who knows exactly what’s in your book and can recommend specific chapters when people ask questions. We’re making it easy for the AI librarian to understand and recommend your content.”
Or: “AI search is like having a knowledgeable friend who’s read everything online. When someone asks that friend a question, they pull information from the best sources to give a complete answer. We’re making sure your business is one of those trusted sources your AI friend recommends.”
Address common concerns:
Client concern: “Isn’t this just another trend? We’ve already tried SEO and didn’t see results.”
Response: “AI SEO isn’t separate from SEO, it’s how search works now. Google already uses AI in search; this isn’t something coming in the future. We’re adapting to how search already works today. The old SEO approaches you tried were competing to rank on page one. AI SEO ensures you appear in the AI-generated answers above position one. This is more important than traditional rankings.”
Client concern: “This sounds expensive. We’re a small business.”
Response: “AI SEO doesn’t require huge budgets. The core work is organizing your existing content better, adding structure that helps AI understand what you offer, and ensuring your information is consistent everywhere online. We can start with your top three service pages and one comprehensive article, see results, then expand from there. The approach scales with your budget.”
Client concern: “How long until we see results?”
Response: “Honest timeline: 2-3 months before you start appearing in AI answers and featured snippets for your target questions. 6 months to build strong visibility. This isn’t instant, but it’s building a foundation that compounds over time. Traditional advertising stops working when you stop paying. AI SEO visibility continues working and often gets stronger as you add more optimized content.”
Create simple progress reports:
Instead of technical metrics, report in business language:
“This month, your company appeared in AI-generated answers 23 times when people searched for [relevant topics]. Your accounting services page now appears in the featured snippet for ‘accounting services for restaurants Malaysia’. We’re seeing 34% more people finding your website through question-based searches like ‘how to’ and ‘what is’.”
Include screenshots of where they appear, highlight questions they’re now ranking for, and connect metrics to business impact: “These question searches typically convert at 12% compared to 6% for regular keyword searches, meaning more of your website visitors become actual leads.”
Make it collaborative:
Position AI SEO as a partnership, not a service you do to their website:
“We need your expertise. You know what questions customers ask when they call. You know what concerns they have. You know what makes your service different from competitors. We’ll take that knowledge and structure it in a way that AI systems understand and share with potential customers. This isn’t just technical work, it’s translating your expertise into formats that reach more people.”
This framing respects their domain knowledge while positioning your agency as the technical translator making that knowledge more accessible.
The key to explaining AI SEO to non-technical Malaysian clients: avoid jargon, focus relentlessly on business outcomes, use concrete examples and visuals, acknowledge their concerns directly, and position AI SEO as the adaptation to how search already works rather than a speculative bet on the future. When clients understand that AI SEO addresses real problems they’re experiencing now, competitors appearing in answer boxes while they don’t, customers asking informed questions that suggest they’ve researched competitors, traffic coming from traditional search but not converting, they recognize the value without needing to understand the technical details.
The Path Forward With AI SEO In Malaysia
The evolution of search toward AI-powered understanding and generation isn’t slowing. Google continues refining MUM and subsequent models. AI assistants like ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity grow in popularity. Malaysians increasingly search using voice, social platforms, and conversational interfaces.
For Malaysian businesses, AI SEO represents not an additional marketing tactic but a fundamental shift in how you structure, present, and validate your online presence. The businesses thriving in this environment share common characteristics: they provide genuinely helpful, comprehensive information; they make that information easily accessible and understandable to both humans and AI systems; they establish clear entity identity with consistent information across platforms; and they demonstrate expertise and trustworthiness through concrete evidence.
The advantage for Malaysian businesses willing to embrace AI SEO now is significant. Most competitors remain focused on traditional SEO tactics that are increasingly less effective. Featured snippets, AI overviews, and answer box positions remain relatively uncontested compared to traditional organic rankings. Early adopters establish authority that becomes harder for later entrants to displace.
Start where you are. If you’ve read this guide, you understand more about AI SEO than most Malaysian business owners and many SEO practitioners. Choose one high-value service or topic area. Implement the framework: clear entity definition, question-based content structure, proper schema markup, comprehensive topical coverage, trust signals. Monitor results. Refine based on what works. Expand systematically.
The question isn’t whether AI search will dominate, it already does for millions of searches daily. The question is whether your business will be visible, cited, and recommended when potential customers search for solutions you provide. The answer depends on actions you take starting today.
Simple Action Checklist For Malaysian Business Owners:
- Define your entity: Write a clear 200-word description of your business, services, and target customers. List your top 5 services and primary service locations.
- Identify customer questions: List 20-30 questions prospects ask before buying. Include questions in English and Bahasa Malaysia if your customers speak both languages.
- Optimize one priority page: Take your top revenue-generating service page. Restructure it with question-based H2 headings, direct answer paragraphs, comprehensive information, and proper schema markup (Organization + LocalBusiness + Service + FAQPage).
- Ensure consistency: Verify your business name, address, phone, and services match exactly across your website, Google Business Profile, and social media.
- Monitor and iterate: Set a monthly reminder to check Search Console for question queries you’re appearing for. Add one new optimized page or article each month addressing another customer question.
Detailed Action Checklist For Malaysian Agencies and SEO Teams:
- Conduct AI readiness audit: For each client, assess current schema implementation, content structure for extraction, entity clarity, trust signals, and technical foundation. Identify gaps prioritized by revenue impact.
- Build question database: Use Search Console, Ahrefs/SEMrush, People Also Ask, and client conversations to compile 100+ questions relevant to each client’s business.
- Create optimization templates: Develop page templates for service pages, blog articles, FAQ pages, and location pages that incorporate question-based structure, proper schema, and AI-ready formatting.
- Implement schema framework: Roll out Organization schema across all clients. Add LocalBusiness, Service, Product, and FAQPage schema to relevant pages. Validate all implementations and monitor in Search Console.
- Build topical authority clusters: For each client’s core money topics, create pillar pages with comprehensive coverage and supporting articles addressing specific aspects. Interlink strategically.
- Establish monitoring systems: Set up tracking for featured snippets, PAA appearances, AI overview citations, question-query traffic, and schema validation. Create client-friendly reporting formats that connect metrics to business value.
- Develop client education materials: Create simple explanations, visual examples, and case studies that help non-technical clients understand AI SEO value without drowning in jargon.
- Stay current: AI search evolution continues. Set monthly time to test new search features, monitor industry discussions, and adjust strategies based on observed changes in AI result formatting and citation patterns.
The future of search in Malaysia is multilingual, conversational, AI-powered, and mobile-first. Businesses that adapt their digital presence to this reality will capture the attention, trust, and business of customers navigating this new search landscape. The framework exists. The tools are accessible. The opportunity is immediate. Your move determines whether you lead or follow in Malaysia’s AI-powered search environment.
Reach out for AI SEO services for your brand.